The Necessity, Types and Efficacy of Armored Cables
In the complex world of electrical systems, the safety and reliability of cables are of utmost importance. Armored cables, with their unique protective features, play a crucial role in ensuring the stable operation of power transmission and distribution. So, why do cables need to be armored? What types of armored cables are there and what are their respective functions? Let’s explore these questions in detail.
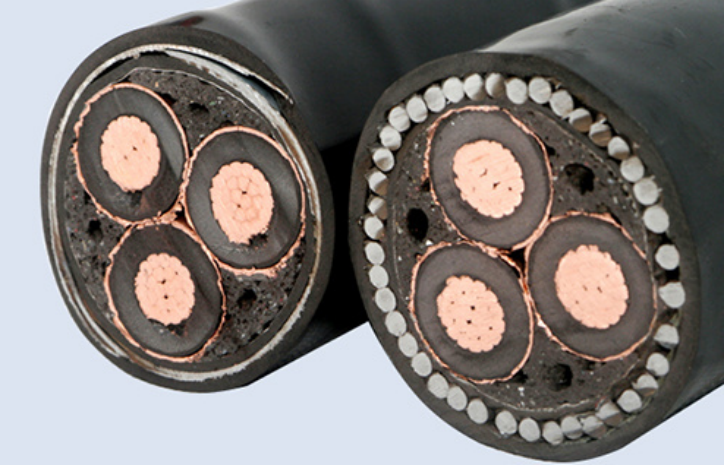
Why Armored Cables Are Needed
Armored cables are designed to provide enhanced protection to the cable core. In many scenarios, cables are exposed to various risks that can lead to accidental damage. For example, when cables are buried directly underground for outdoor installations or laid in tunnels, there is a possibility that the ground may be excavated again in the future. During this process, tools like spades or mechanical excavators may accidentally hit the buried cables. In such cases, the armor layer of the armored cable serves as a shield, protecting the cable conductor core from being easily exposed. This not only prevents electric shocks but also ensures the uninterrupted delivery of power. In areas with high mechanical stress or frequent impacts, the use of armored cables becomes even more essential.
Armored cables are designed to provide enhanced protection to the cable core. In many scenarios, cables are exposed to various risks that can lead to accidental damage. For example, when cables are buried directly underground for outdoor installations or laid in tunnels, there is a possibility that the ground may be excavated again in the future. During this process, tools like spades or mechanical excavators may accidentally hit the buried cables. In such cases, the armor layer of the armored cable serves as a shield, protecting the cable conductor core from being easily exposed. This not only prevents electric shocks but also ensures the uninterrupted delivery of power. In areas with high mechanical stress or frequent impacts, the use of armored cables becomes even more essential.
Types of Armored Cables and Their Efficacy
Steel Wire Armored (SWA) Cables
Steel wire armored cables are constructed with multiple strands of steel wire wound around the cable core. Steel is a strong and durable material, which gives these cables excellent mechanical protection. SWA cables are highly resistant to tensile forces, making them suitable for applications where the cable needs to withstand pulling or stretching. For instance, in vertical installations such as in high – rise buildings’ elevator shafts or in long – distance overhead power lines, SWA cables can effectively bear the weight of the cable itself and any additional tension caused by external factors. They are also commonly used in harsh industrial environments where there may be vibrations, impacts, or rough handling. The steel wire armor can protect the cable from being cut, crushed, or damaged by sharp objects, thus ensuring the long – term reliable operation of the cable.
Steel Tape Armored (STA) Cables
STA cables have a layer of steel tape wrapped around the cable core. The steel tape provides good protection against radial pressure. These cables are often used in applications where the cable needs to be buried directly in the ground. The steel tape can withstand the pressure from the soil and any heavy objects that may be placed on the ground above the cable. In urban power distribution systems, STA cables are widely used for underground cable networks. They can be laid in trenches and are able to resist the forces exerted by the backfill soil. STA cables are also suitable for use in tunnels and ducts, where they need to protect the inner conductors from external mechanical forces while maintaining a relatively compact size compared to some other types of armored cables.
Aluminum Wire Armored (AWA) Cables
Aluminum wire armored cables use aluminum wires as the armor material. One of the key advantages of AWA cables is that aluminum is non – magnetic. In single – core cables, if steel wire armor is used, when current flows through the cable, a magnetic field will be induced, which can cause overheating and a reduction in the cable’s performance due to the generation of eddy currents in the steel. AWA cables avoid this problem. They are often used in applications where magnetic interference needs to be minimized, such as in certain sensitive electrical equipment or in areas with a high – density electromagnetic environment. Additionally, aluminum is relatively lightweight compared to steel, which can make AWA cables easier to install and handle, especially in situations where long lengths of cable need to be deployed.
Aluminum Tape Armored (ATA) Cables
ATA cables feature a layer of aluminum tape wrapped around the cable core. Similar to AWA cables, ATA cables benefit from the non – magnetic properties of aluminum. The aluminum tape provides protection against external mechanical forces, such as minor impacts and abrasion. They are suitable for applications where a balance between mechanical protection and resistance to magnetic interference is required. In some outdoor communication cable installations or in low – voltage power distribution systems in areas with electromagnetic concerns, ATA cables can be a good choice. The aluminum tape also offers some level of corrosion resistance, which is beneficial for cables operating in outdoor or humid environments.
In conclusion, armored cables are an essential part of modern electrical systems. Their ability to protect against mechanical damage, corrosion, and in some cases, magnetic interference, makes them suitable for a wide range of applications. Whether it’s the strength of steel – based armored cables or the non – magnetic advantages of aluminum – based ones, each type of armored cable has its own unique features that meet the diverse needs of different industries and installation scenarios. By understanding the necessity and characteristics of these cables, we can make more informed decisions when it comes to cable selection and installation, ensuring the safety and efficiency of our electrical infrastructure.
